Prognosis of colon cancer
Most patients are worried about the prognosis of colon cancer. Currently, there are several different ways to assess the patient’s prognosis, the most important of which is the analysis of the stage of the disease.
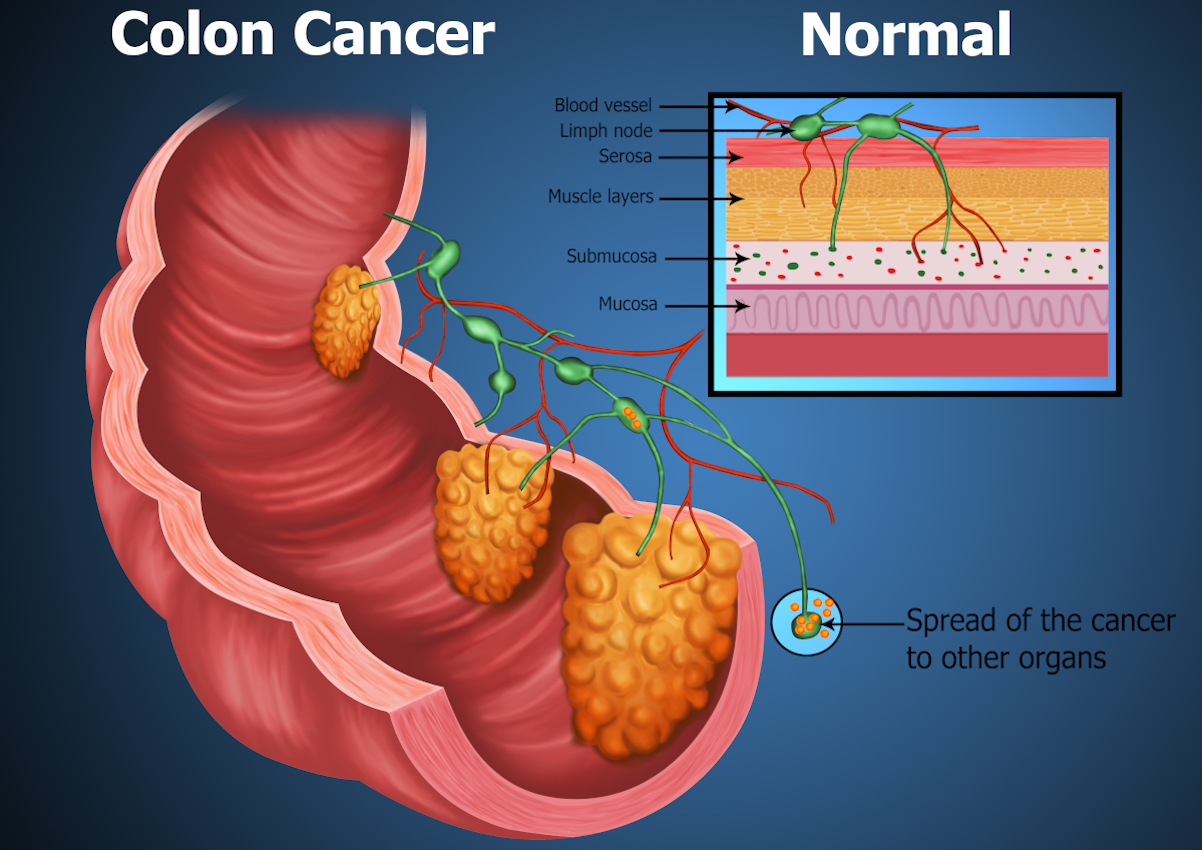
Stages
There are four stages of colon cancer:
- Stage 0: This is the earliest stage of colon cancer, where the cancer is only present in the innermost lining of the colon.
- Stage I: In this stage, the cancer has grown through the inner lining of the colon and may have spread to the next layer of tissue but has not reached the lymph nodes or other organs.
- Stage II: The cancer has spread beyond the colon wall into the surrounding tissues but has not reached the lymph nodes.
- Stage III: At this stage, the cancer has spread to the nearby lymph nodes but has not reached other distant parts of the body.
- Stage IV: This is the most advanced stage of colon cancer, where the cancer has spread to distant organs or tissues, such as the liver, lungs, or other parts of the body.
Prognosis
The prognosis of colon cancer depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient's overall health, and the response to treatment. Generally, the earlier the stage at diagnosis, the better the prognosis.
Treatment options for colon cancer may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy. The specific treatment plan is tailored to each individual based on the stage and other factors.
Treatment Options
The treatment options for colon cancer depend on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient's overall health, and their preferences. The primary treatment methods include:
- Surgery: Surgery is often the main treatment for colon cancer. It involves removing the cancerous tumor along with a margin of healthy tissue. In some cases, nearby lymph nodes may also be removed.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be administered before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) to shrink tumors, after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) to kill remaining cancer cells, or in advanced cases to control the spread of cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells. It may be used in combination with surgery or chemotherapy, especially for rectal cancer.
- Targeted Therapies: Targeted therapies are drugs that specifically target certain molecules involved in cancer growth. They work by interfering with specific pathways or signals that promote cancer cell growth and division.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy helps the body's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. It can be used in certain cases of advanced colon cancer.
The treatment plan for an individual with colon cancer is determined by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, and other specialists. The team considers the specific characteristics of the cancer, the patient's overall health, and their preferences to develop the most appropriate treatment approach.
Follow-up and Survivorship
After completing treatment for colon cancer, regular follow-up visits are important to monitor for any signs of recurrence or new cancer growth. These visits may include physical examinations, imaging tests, blood tests, and other evaluations as needed. It's essential for individuals to communicate any new symptoms or concerns to their healthcare team.
Survivorship programs and support groups can provide valuable resources and emotional support for individuals who have completed treatment for colon cancer. These programs address various aspects of recovery, including physical and emotional well-being, healthy lifestyle choices, and management of potential long-term effects of treatment.
Prevention and Early Detection
While not all cases of colon cancer can be prevented, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk and detect the disease early:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding tobacco can help reduce the risk of developing colon cancer.
- Get screened: Regular screening tests, such as colonoscopies, can help detect precancerous polyps or early-stage colon cancer. The recommended age to start screening may vary depending on individual risk factors, so it's important to consult with a healthcare professional.
- Be aware of symptoms: Knowing the signs and symptoms of colon cancer, such as changes in bowel habits, rectal bleeding, persistent abdominal discomfort, and unexplained weight loss, can prompt early medical evaluation and diagnosis.
By adopting healthy lifestyle choices and undergoing regular screenings, individuals can improve their chances of preventing colon cancer or detecting it at an early stage when treatment is most effective.
Support and Treatment
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with colon cancer, it's important to seek appropriate medical treatment and support. Here are some key points to consider:
- Consult with healthcare professionals: Work closely with oncologists, surgeons, and other healthcare providers specializing in colorectal cancer to develop an individualized treatment plan.
- Consider treatment options: Treatment for colon cancer may involve surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these approaches. The specific treatment plan will depend on factors such as the stage and location of the cancer.
- Seek emotional support: Dealing with a cancer diagnosis can be emotionally challenging. Reach out to support groups, counseling services, or online communities to connect with others facing similar experiences.
Remember that each individual's journey with colon cancer is unique, and it's important to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the best course of action.
Conclusion
Colon cancer is a serious condition that requires medical attention and support. By understanding its risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps towards prevention, early detection, and effective management. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and support throughout your journey.
Resources and Additional Information
Here are some additional resources and information to learn more about colon cancer:
- American Cancer Society - Colon and Rectal Cancer
- National Cancer Institute - Colorectal Cancer
- Parkland Natural Health Clinic - Anti-Candida Colon Hydrotherapy
Disclaimer
The information provided on this website is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, please consult a qualified healthcare provider.
Comments
Post a Comment